A scroll view is a type of component that enables you to view content that is not able to be displayed in one screen. This means you can scroll content either vertically or horizontally. Basically every website or app requires that capability.
In React Native, there are two different types of basic scroll views. The ScrollView renders all child components at once, making it good for scenarios where you don't have a huge lists of elements.
The FlatList is another component, that renders the elements according to the data that you provide. This can lead to better performance in some cases. I will make a separate post comparing those two.
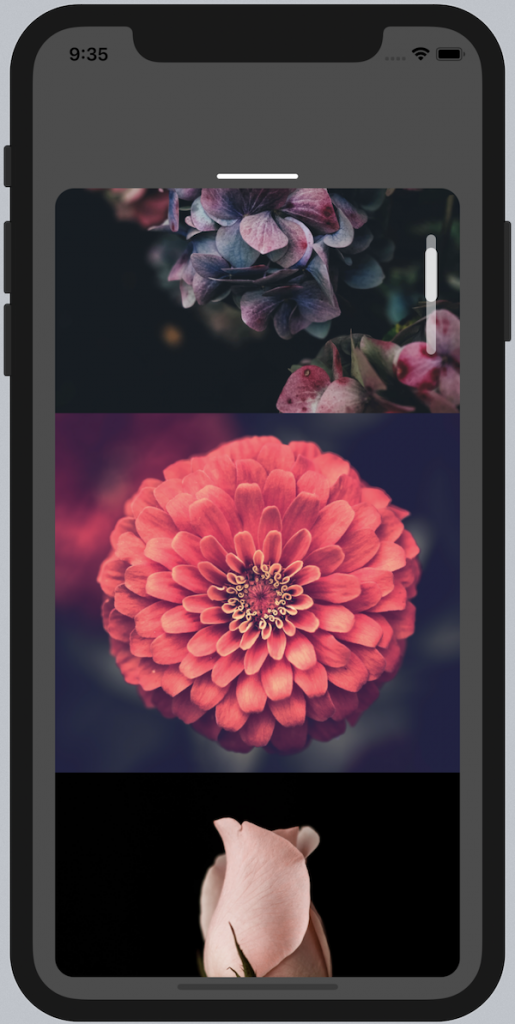
Scroll Indicator Start Position
A scroll indicator or scroll bar shows you the current scroll location of the content inside the scroll view. But the standard scroll indicator looks rather simple. To improve the visual impression and user experience of your app, you may want to change the default style.
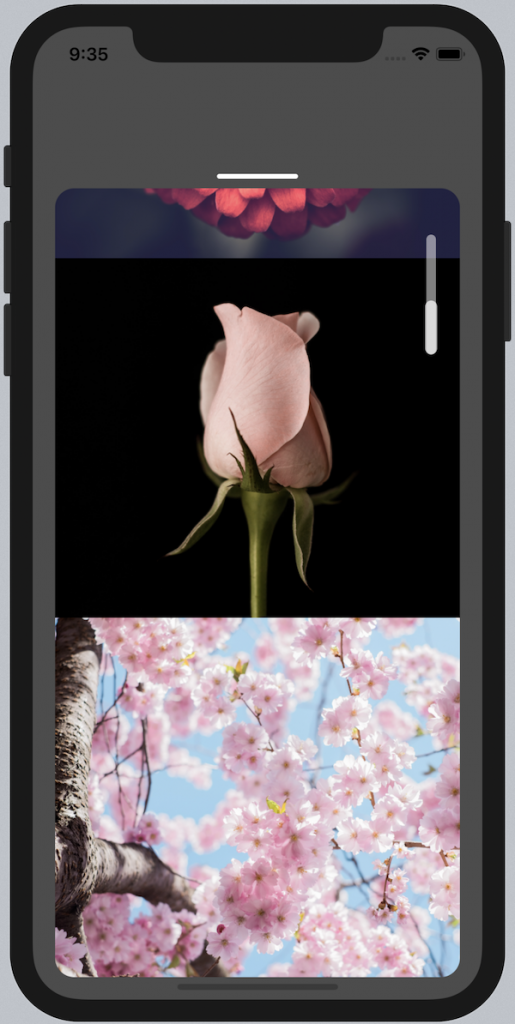
Scroll Indicator End Position
Both ScrollView and FlatList provide functionality for creating your own scroll indicator. To disable the default scroll indicator you need to use the showsVerticalScrollIndicator or showsHorizontalScrollIndicator prop.
Then, you need to track the content offset of the scroll view, as it changes when scrolling. For that, you can use the onScroll callback, in which you save the offset.
After that works, you want to know the actual size of the scroll view's (scrollable) content, in order to calculate the position. For that, you can use the onContentSizeChange callback, and save the value (height / width).
| export default Example = () => { | |
| const [contentOffset, setContentOffset] = React.useState({ x: 0, y: 0 }); | |
| const [contentSize, setContentSize] = React.useState(0); | |
| return( | |
| <ScrollView | |
| onScroll={e => { | |
| setContentOffset(e.nativeEvent.contentOffset); | |
| }} | |
| onContentSizeChange={(_, height) => { | |
| setContentSize(height); | |
| }} | |
| >... | |
| </ScrollView> | |
| ); | |
| } |
When testing, you may have realized that, when scrolling down, the end position of the content offset does not match the scroll content size. The trick there is to additionally take the size of the scroll view itself, which is the missing part. You can retrieve this value by using the onLayout callback, which can be used on any React Native View to get its measurements.
| const scrollElementHeightPercent = 45; | |
| export default Example = () => { | |
| ... | |
| const [scrollViewHeight, setScrollViewHeight] = React.useState(0); | |
| const scrollPerc = (contentOffset.y / (contentSize - scrollViewHeight)) | |
| * (100 - scrollElementHeightPercent); | |
| return( | |
| <ScrollView | |
| ... | |
| onLayout={e => { | |
| setScrollViewHeight(e.nativeEvent.layout.height); | |
| }} | |
| >... | |
| </ScrollView> | |
| ); | |
| } |
Finally, the content size will be subtracted by the scroll view size, and the calculation should be correct. The actually height of the scroll indicator is defined as scrollElementHeightPercent, which relates to its parent view's size, the scroll bar.
| <View | |
| style={{ | |
| height: 100, | |
| ... | |
| }} | |
| > | |
| <View | |
| style={{ | |
| position: "absolute", | |
| top: `${Number(scrollPerc || 0).toFixed(0)}%`, | |
| height: `${scrollElementHeightPercent}%` | |
| ... | |
| }} | |
| /> | |
| </View> |
The scroll indicator component then works by using absolute positioning, top and height percentages.
You can find the source code here.